Data Structure and Algorithms based on the Object-oriented programming
(OOP) where some are the base of OOP for instant inheritance,
polymorphism, Encapsulation and Abstraction etc. Now we will start learning
data structures in Programming languages such as Linked list, arrays, Structs,
Classes, Queues, Stacks etc.
Today’s Concept:
Queue Data Structure
Prerequisite of this Lab is all those students who have basic concepts on
C++ Programming such as Syntax of Language, concept of functions, pointers,
datatypes etc. Visual Studio 2012 and onward version will be used for
implementation and programming tasks assigned in the Lab.
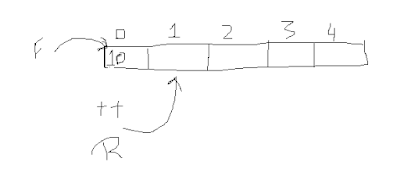
Queue Data Structure can be implemented using C++ or any
other programming languages. This is also known as a linear data structure
because they use to store data in contiguous memory blocks just like single
data structure Arrays stored their data. Queue works in FIFO (first in first
out ) principle by this it means any values which enters first will print first
for example if we enter 1,2,3,4 in the queue then we will get 1 then 2 and so
on you can take example of passengers who waits for the bus or a line in banks
to deposit amount any person who comes first serves first.
Operations in Queue:
There are different operations in Queue such as:
- EnQueue use to Enter value in Queue
- DeQueue use to remove value from Queue
- IsFull() check the full status of Queue
- IsEmpty() use to check the empty status of queue
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class queue
{
int *q,maxsize,rear,fornt;
public:
queue(int size)
{
this->q=new int(size);
maxsize=size;
rear=-1;
fornt=-1;
}
bool isfull()
{
if(this->rear==maxsize-1)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool isEmpty()
{
if(this->rear==-1)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void enqueu(int value)
{
if(this->isfull())
{
cout<<"Queue is full"<<endl;
}
else
{
++rear;
if(rear <= maxsize-1)
{
this->q[rear]=value;
}
else
{
cout<<"no more enteries possible"<<endl;
}
}
}
void deqeue()
{
if(isEmpty())
{
cout<<"Queue is empty"<<endl;
}
else
{
++fornt;
if(this->fornt > rear)
{
cout<<"trying to delete more values than entered"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout<<"Vlaues at front possiton"<< q[this->fornt]<<endl;
}
}
}
};
#include"queue.h"
int main()
{
queue obj(5);
obj.enqueu(10);
obj.enqueu(20);
obj.enqueu(30);
obj.enqueu(40);
obj.enqueu(50);
obj.enqueu(50);
obj.deqeue();
obj.deqeue();
obj.deqeue();
obj.deqeue();
obj.deqeue();
obj.deqeue();
return 0;
}
Lab Task Activity Queue:
- Write your understanding on the word document about linked list using C++ please read the manual and just write what you understand don't try to copy and past from other sources.
- Create C++ program to run same code given as Example and take screenshot for submission.
- You have learnt linked list single and doubly you are instructed to implement FIFO using Linked list of your choice single or double.
Click for Submission:





Post a Comment